Harnessing Nature: The Bright Future of Solar Panels
The journey towards a sustainable future has become one of humanity’s most pressing challenges, as the consequences of climate change loom larger. In this context, solar energy has emerged as a beacon of hope. As the world seeks to transition from fossil fuels to renewable sources, solar panels represent a pivotal technology in harnessing nature’s energy. This article explores the remarkable advancements, benefits, and future potential of solar panels, highlighting their transformative role in our energy landscape.
The Essential Role of Solar Energy
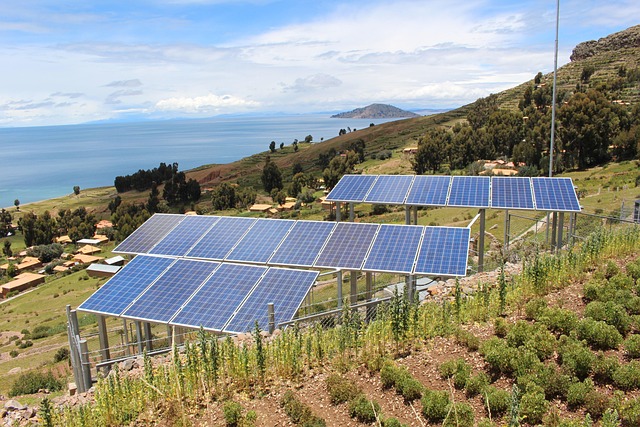
Solar energy, derived from the sun’s rays, is a potent and inexhaustible source of power. Unlike fossil fuels, it is clean, abundant, and available almost everywhere on Earth. The process of converting sunlight into electricity is both simple and effective, involving the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which generate electric current when exposed to sunlight. As research and innovation continue to drive improvements, the efficiency of solar panels has increased significantly, making them a viable alternative to conventional energy sources.
Advancements in Solar Technology
Solar panel technology has made tremendous strides in recent years, driven by both advancements in materials science and an enhanced understanding of solar energy capture mechanisms. One notable development is the emergence of more efficient photovoltaic materials, such as perovskite solar cells. These materials promise higher efficiencies at lower production costs, making solar power even more accessible.
Additionally, innovations in solar panel design have led to the creation of bifacial panels that capture sunlight on both sides, increasing overall energy production. Other advancements include building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), which seamlessly integrate solar technology into the architecture of buildings, further expanding the applicability of solar energy.
Environmental Benefits
The transition to solar energy presents myriad environmental benefits. First and foremost, solar panels produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. This reduction in carbon emissions is crucial in the fight against climate change. According to research, a significant shift to solar energy could substantially lower global carbon emissions, helping to meet international climate targets.
Furthermore, solar energy minimizes water usage compared to traditional energy sources. Power plants that rely on fossil fuels often require vast amounts of water for cooling, whereas solar panels operate independently of such processes, conserving precious water resources.
The Economic Impact
Solar energy has the potential to stimulate economic growth, creating jobs across various sectors. The installation, maintenance, and manufacturing of solar panels require a skilled workforce, leading to new employment opportunities. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the solar sector has already created millions of jobs worldwide, and this number is expected to grow as solar technology continues to expand.
Moreover, as the cost of solar panels continues to decline, more individuals and businesses can invest in solar energy systems. This democratization of access enables homeowners to reduce their energy bills, while businesses can lower operational costs, thereby reinvesting savings into growth and innovation.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government support plays a crucial role in advancing solar energy adoption. Many countries offer various incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and grants, aimed at reducing the upfront costs of solar installation. Legislators are increasingly recognizing the importance of transitioning to renewable energy sources, enacting policies that promote solar adoption as part of broader sustainability goals.
In addition to financial incentives, regulatory frameworks are evolving to facilitate the integration of solar energy into existing power grids. Net metering policies allow homeowners with solar panels to sell excess electricity back to the grid, further incentivizing solar adoption. Such policies create a symbiotic relationship between solar panel owners and local utilities, contributing to a more resilient energy system.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its promising future, the solar industry faces several challenges that must be addressed to ensure sustainable growth. One major issue is the intermittent nature of solar energy generation; energy production fluctuates based on sunlight availability, which raises concerns about reliability during cloudy days or at night.
Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, present a viable solution to this challenge. As battery technology improves and costs decrease, solar energy can be stored for use during low-sunlight periods, ensuring a continuous power supply. Investing in grid infrastructure and smart technologies will also play a vital role in managing and distributing solar energy effectively.
Another challenge lies in the environmental impact of solar panel production and disposal. While solar panels produce clean energy, their manufacturing processes can involve energy-intensive materials and pose recycling challenges at the end of their lifecycle. Research is underway to develop more sustainable production methods as well as effective recycling strategies, ensuring a greener approach to solar energy.
The Future of Solar Energy
As we look to the future, the potential of solar energy seems limitless. Analysts predict that solar power will play a key role in meeting global energy demands, with significant growth extending into the next few decades. Innovations are expected to bring about breakthroughs in efficiency, energy storage, and integration with smart technologies.
Moreover, as awareness of climate issues grows, public demand for clean energy sources will likely amplify. This societal push can spur further investments in solar technology and infrastructure, leading to broader adoption and integration into daily life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar panels represent not just a technology but a vital component in the quest for a sustainable future. As we harness the incredible power of the sun, we open the door to reduced environmental impact, enhanced economic opportunities, and greater energy independence. The path ahead is filled with challenges, yet these obstacles are surmountable through innovation, policy, and public engagement. By embracing solar energy, we can illuminate a bright and sustainable future for generations to come.